Eskom mandate, vision and mission
Eskom Holdings SOC Ltd is a state-owned corporation (SOC) as defined by the Companies Act 71 of 2008. It is entirely owned by the South African government, with the Minister of Electricity and Energy serving as the Shareholder representative. Eskom operates across the electricity value chain, providing generation, transmission, and distribution services within South Africa, and participates in electricity trading within the Southern African Development Community (SADC).
Eskom has a dual mandate to drive both commercial and socio-economic objectives. This ensures that the company remains reliable and financially sustainable while contributing to the growth of the South African economy and transitioning responsibly to a lower-carbon future. The mandate is set out in the Memorandum of Incorporation (MOI) which is provided by the Eskom Board and accepted by the Shareholder. The
vision and mission were developed to support Eskom’s mandate. The four Strategic Objectives of Eskom have been developed to achieve the
mandate, vision, and mission in alignment with the five strategic priorities defined by the Shareholder.
Eskom’s business model, operating structure, and footprint
Eskom creates value through the generation, transmission, distribution, purchase, and sale of electricity. Its value creation model below depicts how it transforms inputs into electricity supplied to customers. Electricity is generated by transforming inputs from the natural environment, such as coal, nuclear fuel, fuel oil, and diesel, as well as water and wind, into electricity. This energy is transmitted over Eskom’s ~33 000km of network in which the supply and demand of electricity are balanced in real time, maintaining the frequency of the power system at 50 hertz (Hz). The electricity is distributed through an extensive distribution network that covers the entire country to supply over 86% of South Africa’s needs and ~20% of the electricity produced in Africa.
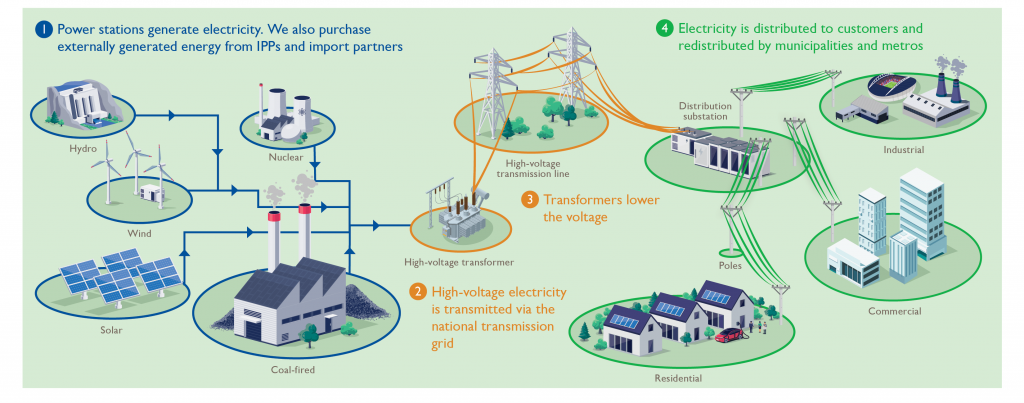
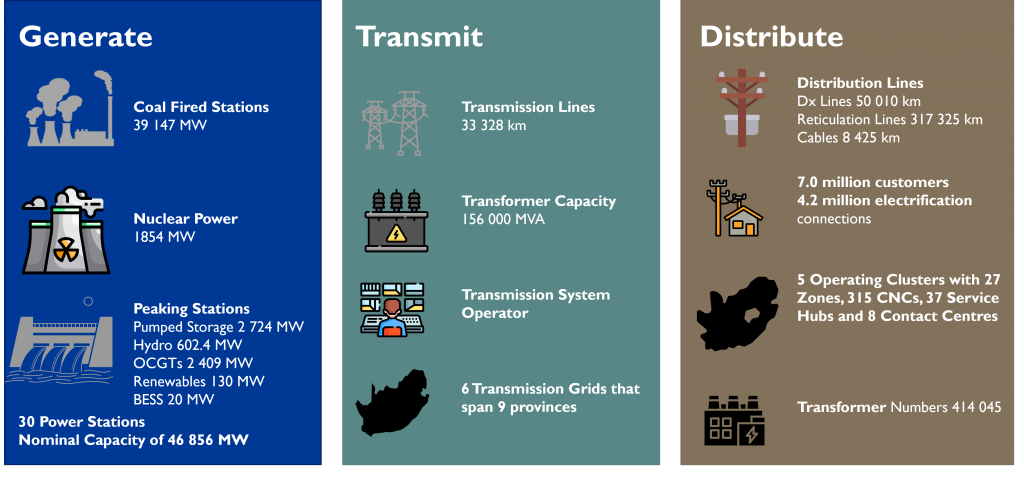
The electricity is generated by 30 power stations with a total nominal capacity of ~47GW. The electricity is then transmitted over a ~33 328km transmission network which balances the supply and demand in real-time and maintains the frequency of the power system at 50 hertz (Hz). The electricity is distributed through an extensive distribution network that covers the entire country to supply over 86% of South Africa’s needs and ~20% of the electricity generated in Africa. Eskom’s footprint and asset base are shown in the figure below.
Operating structure
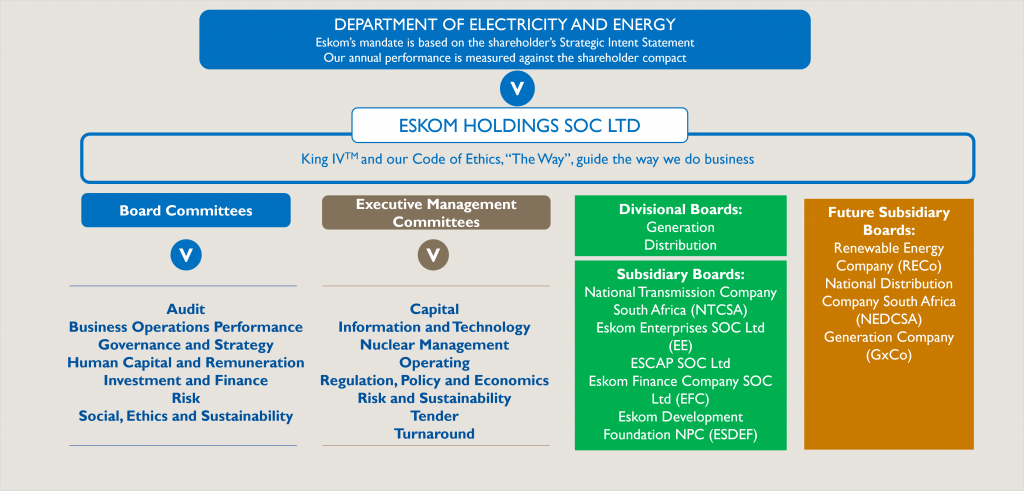
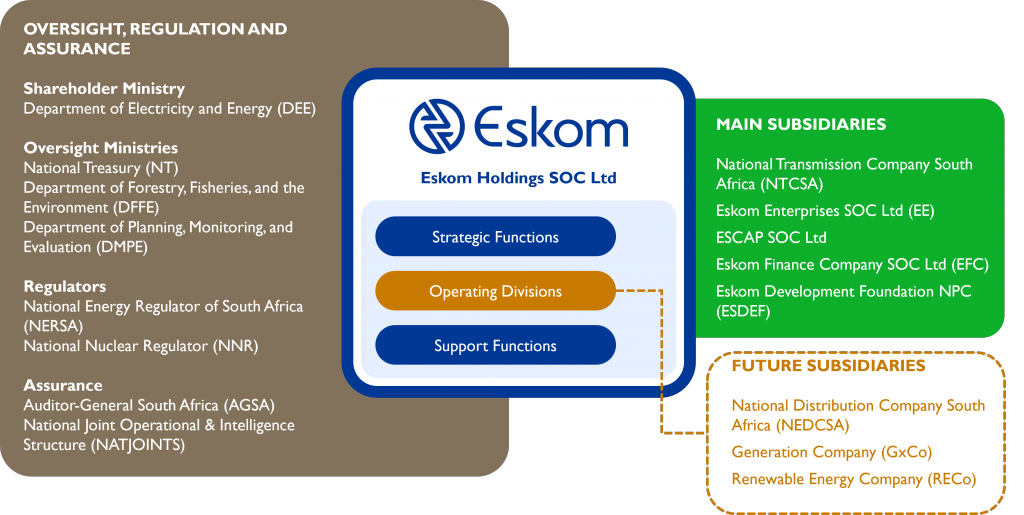
Following South Africa’s democratic elections in May 2024, the seventh administration introduced significant structural reforms including the establishment of the Department of Electricity and Energy (DEE). With this reorganisation, state-owned enterprises previously under the
Department of Public Enterprises (DPE) were reassigned to relevant line-function ministries, which now hold full Shareholder responsibility.
As a result, the Minister of Electricity and Energy assumed the role of the Shareholder representative for Eskom. As a Shareholder Ministry, the DEE outlines the expectations from the government, oversees performance and sets energy policy. Key documents such as the Integrated Resource Plan (IRP), the Electricity Regulation Act (ERA) and the Electricity Pricing Policy (EPP) are instruments that outline the direction of the electricity sector in which Eskom operates.
The National Energy Regulator of South Africa (NERSA) regulates Eskom’s activities, including tariff determination and approval, while the National Nuclear Regulator (NRR) oversees nuclear safety at Koeberg. Eskom is also subject to oversight or regulation by several other government departments (e.g., National Treasury (NT), Department of Planning, Monitoring and Evaluation, Department of Forestry, Fisheries, and the Environment (DFFE)), and Parliamentary committees.
The figure below provides Eskom’s high-level organisational and regulatory structure.
Company Disclosure Information
- Other related company information can be accessed by logging a request with the Office of the Company Secretary.